RENMIN UNIVERSITY of CHINA



As an important driving force for advancing human civilization and promoting world peace and development, mutual learning among civilizations holds special significance in our times, as the world faces unprecedented changes unseen in a century. This section examines global respondents' attitudes toward concepts such as civilizational diversity, common values of all humanity, civilizational inheritance and innovation, and international people-to-people exchanges and cooperation. It analyzes the international community's acceptance and value recognition of ideas related to mutual learning among civilizations, thereby providing deeper insights into the conceptual foundation for harmonious coexistence among different civilizations.
I.Global Perspectives on Civilizational Diversity
Respondents generally embrace the value concept of cultural pluralism and the principle of equality. The data shows that 90% of respondents recognize that the diversity of world cultures constitutes an important treasure of human society, while 87.7% agree that all cultures should be treated equally without labeling some as advanced and others as backward. Additionally, 85.4% believe that cultural diversity is as significant to human progress as biodiversity is to ecosystems. Meanwhile, 80.6% consider that positioning one's own culture as superior to others is detrimental to international relations, 86.6% view attempts to forcibly change other countries' cultural traditions as disrespectful, and 88.1% agree that no country should impose its values on others.
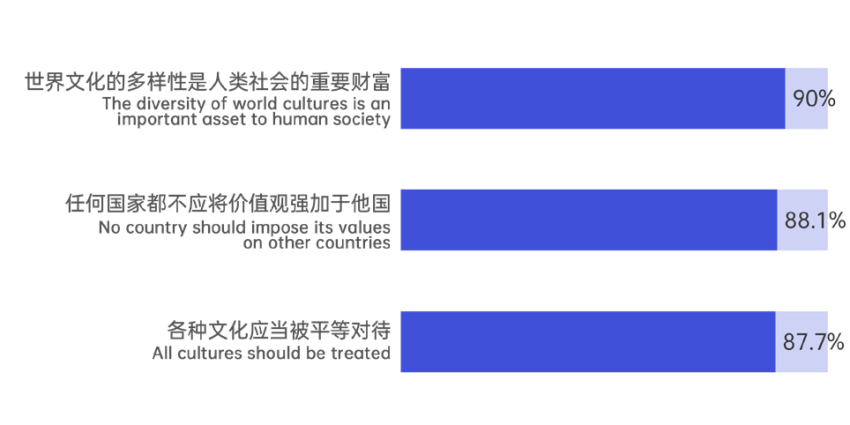
Figure 1.1 Level of Agreement with Views on Civilizational Diversity
Respondents demonstrate strong agreement regarding countries' right to choose their development paths and approaches to handling cultural differences. 88.8% believe that all countries have the right to choose development paths and social systems suited to their national conditions, 91.2% consider that international relations should respect cultural differences and traditions, and 87.7% believe that differences in culture and values should not serve as grounds for international conflicts. Regarding cultural protection in the process of globalization, 85.7% believe that globalization should protect cultural diversity rather than lead to cultural homogenization, 90.8% agree that respecting diversity is a fundamental principle that global society should follow, and 80% believe that dividing the world into opposing camps and distinguishing between friends and foes based on values will hinder international exchanges and cooperation.
These findings reflect that people worldwide value civilizational diversity and recognize that each civilization is rooted in specific conditions, embodying the extraordinary wisdom and spiritual pursuits of a nation and its people, with every type of civilization and culture possessing inherent value. The global public has generally rejected theories of civilizational superiority and civilizational clash, acknowledging that there are no universally applicable civilizational standards and that any attempt to resolve civilizational differences through coercive means is harmful. Comprehensive respect should be maintained for the soil from which civilizations emerge and their uniqueness, the creators of civilizations and their ways of thinking, as well as the historical role of civilizations and the continuity of their influence.
II. Global Consensus on Common Values for All Humanity
The global public also demonstrates widespread agreement with common values for all humanity such as peace and development. 87.7% agree that peaceful development is a shared aspiration of peoples across all nations, 84.5% believe that countries should avoid zero-sum thinking and pursue common development, and 90.2% agree that global challenges require a collective response from all nations, with no country able to remain unaffected.
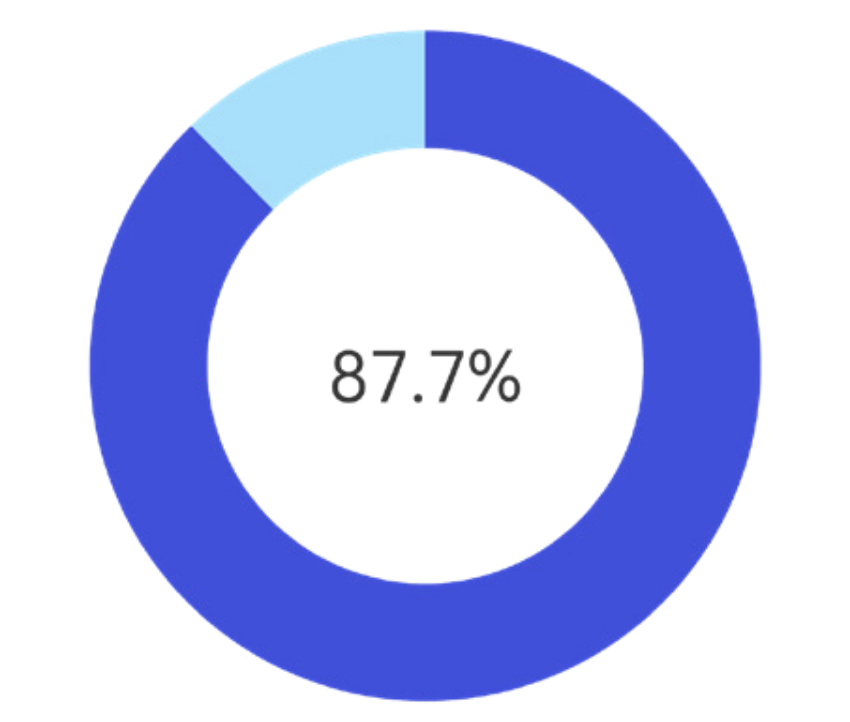
Figure 1.2 Proportion of Respondents Who Agree That Peaceful Development Is a Shared Aspiration of All Peoples
To achieve common values for all humanity, respondents believe it is necessary to transcend ideological differences and promote mutual learning among civilizations.
91.8% believe that relations between different cultures should be primarily based on win-win cooperation rather than confrontation, 81% recognize the necessity of setting aside ideological prejudices and respecting cultural diversity, and 88.7% consider equal dialogue to be the best approach for resolving international differences, reflecting respondents' rational understanding of transcending ideological divisions and seeking common ground in values. 88.6% believe that differences between cultures can serve as motivation for mutual learning and common progress, 89.5% consider cultural exchanges to provide an important foundation for establishing international cooperation, 87.3% believe that international transportation and infrastructure development help promote cultural exchanges between different countries, and 87.4% believe that cultural dialogue can effectively reduce international conflicts and promote world peace.
The aforementioned findings indicate that despite differences in historical cultures and social systems among nations, there exists broad consensus in the pursuit of common values for all humanity such as peace, development, equity, justice, democracy, and freedom. Respondents profoundly recognize that these values embody the consensus of different civilizations and represent the greatest common denominator of universally recognized value concepts, transcending differences in ideology, social systems, and development levels. They provide a value bond for achieving the broadest unity in the international community and reflect the value foundation and spiritual support needed for building a community with a shared future for mankind.
III. Global Cognitive Landscape of Civilizational Heritage and Innovation
Respondents highly recognize the dynamic and innovative characteristics of civilizational development and profoundly understand the dialectical relationship between heritage and innovation. 88.5% believe that cultural innovation is as important as traditional preservation, 87.1% consider that modernization does not mean abandoning tradition but rather represents innovative development of tradition, and 80.9% agree that regular renewal of cultural traditions is a necessary condition for sustained cultural development. Respondents' recognition of civilizational innovation and development is also reflected in their understanding of national cultural confidence: 88.3% believe that when a country truly values its own culture, it creates powerful spiritual forces that promote its growth and development.

Figure 1.3 Level of Agreement with Views on Civilizational Heritage and Innovation
Respondents express high recognition for the integration of modernization with cultural traditions. 82.9% believe that modern development theories should be integrated with their country's cultural traditions, 85.2% consider that there may be points of convergence between different development concepts and their national cultural traditions, 82.2% believe that the integration of theory and tradition is crucial to a country's development path, and 80.6% believe that such integration should creatively generate new cultural vitality. Respondents also show high recognition for the diversity of modernization paths, with 83.4% believing that each country's modernization path should be based on its own cultural traditions, and 85.9% believing that different countries' modernization practices enrich the diversity of human civilization.
These findings demonstrate respondents' profound understanding of the laws governing civilizational heritage and development, recognizing that any civilization must keep pace with the times and continuously absorb the essence of each era. Respondents generally recognize that cultural exchanges and mutual learning require both inheriting and promoting the excellent traditional culture of one's own nation and advancing with the times through innovation, achieving sustained civilizational prosperity through creative transformation and innovative development. This understanding reflects comprehension of practices such as the project for inheriting and developing excellent traditional Chinese culture, embodying the fundamental law that civilizations develop through innovation and endure through heritage.
IV. Global Public Expectations for Strengthening International Humanities Exchange and Cooperation
Global respondents demonstrate high recognition of the importance of humanities exchanges and their role as practical pathways for promoting mutual learning among civilizations. 89.8% believe that exchanges and interactions between different cultures can promote common human progress, 89.5% consider that cultural exchanges provide an important foundation for establishing international cooperation, and 89.4% agree that international humanities exchanges help enhance mutual understanding among peoples of different countries.
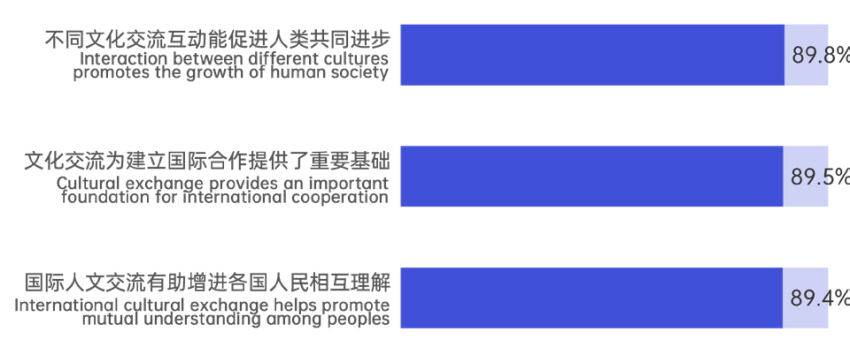
Figure 1.4 Level of Agreement with Views on Strengthening International Humanities Exchange and Cooperation
Respondents demonstrate high consensus regarding the positive effects of cultural exchanges. 87.9% believe that appreciating and learning from the strengths of other cultures helps enrich one's own culture, 87.5% consider that open exchanges between cultures are more conducive to social development than isolation between civilizations, and 84.6% believe that in-depth interpersonal interactions can effectively reduce cultural misunderstandings and prejudices.
These data reflect respondents' profound understanding of the fundamental principle that "civilizations become colorful through exchanges and enriched through mutual learning," recognizing that humanities exchanges, as an important pathway for eliminating barriers and misunderstandings while promoting people-to-people connectivity, possess foundational, extensive, pioneering, and enduring characteristics. Respondents generally acknowledge that people serve as the best vehicles for cultural exchanges and mutual learning, and that extensive cooperation in education, culture, sports, health, and other fields can effectively advance various forms of humanities exchanges to greater depth and substance, creating better conditions for promoting cultural exchanges and mutual learning. This reflects their profound understanding and positive expectations for building a global network of civilizational dialogue and cooperation and fostering mutual understanding and affinity among peoples of all countries.