RENMIN UNIVERSITY of CHINA



Global populations maintain an open and receptive attitude toward foreign civilizations and cultural elements, engaging in selective absorption based on practical considerations. Against this backdrop, the cognitive status and actual influence of Chinese civilization and culture within the contemporary multicultural exchange framework merit thorough examination. This section systematically presents global populations' cognition, understanding, and attitudes toward Chinese culture, exploring the authentic landscape of Chinese civilization within the international cultural cognitive system and revealing its multidimensional characteristics and cognitive complexity in cross-cultural communication.
I.Global Attention and Cognition of Chinese Culture
Two-thirds of global respondents express interest in Chinese civilization and culture, indicating that Chinese culture has established considerable influence within the international community. Examining attention to specific domains of Chinese culture, 77.2% of respondents show interest in Chinese technology or its applications, demonstrating the international impact of Chinese technology companies' global expansion in recent years. African respondents show the highest attention to Chinese technology at 91.2%, ranking first among all regions, while North America ranks last; approximately 80% of those under 35 years old show such interest. Traditional culture and lifestyle receive relatively similar levels of attention at 63.8% and 63%, respectively, while popular culture receives slightly lower attention at 59.1%. This distribution pattern of attention reflects the outstanding advantages of Chinese technological culture in overseas dissemination, while also demonstrating that traditional culture, lifestyle, and popular culture maintain stable appeal in cross-cultural exchange.
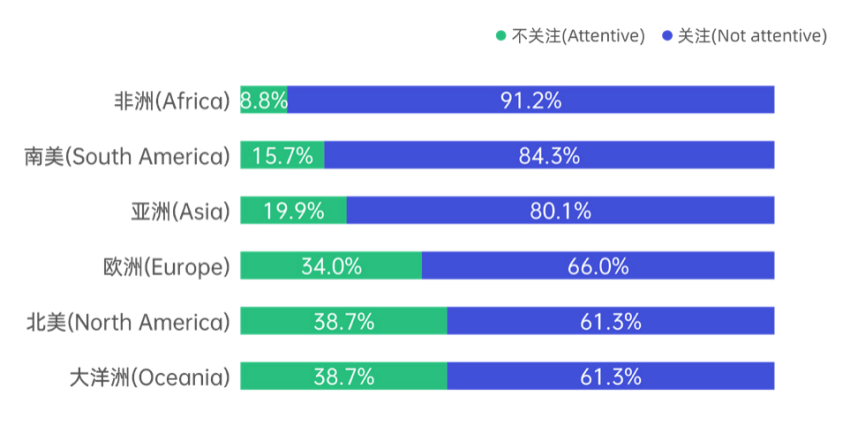
Figure 3.1 Regional Differences in Attention to Chinese Technology
Only 52.8% of respondents consider themselves to understand Chinese culture, while 47.2% express a lack of understanding. It can be observed that the understanding of Chinese culture is 13.7 percentage points lower than the level of attention, revealing the existence of certain cognitive barriers in the transformation process from cultural attention to deep understanding. Comparison of understanding levels across specific domains shows that the technology sector maintains its leading position, with 72.6% expressing understanding of Chinese technology or applications, and the gap between attention and understanding of Chinese technology being merely 4.6 percentage points, demonstrating the high efficiency of technological culture dissemination. Understanding of Chinese lifestyle reaches 59.1%, surpassing traditional culture at 57.3% to rank second, while understanding of popular culture stands at 54.5%. Notably, the gap between attention and understanding in the traditional culture domain reaches 6.5 percentage points, higher than other dimensions, reflecting the variability in cross-cultural cognitive transformation across different cultural fields.
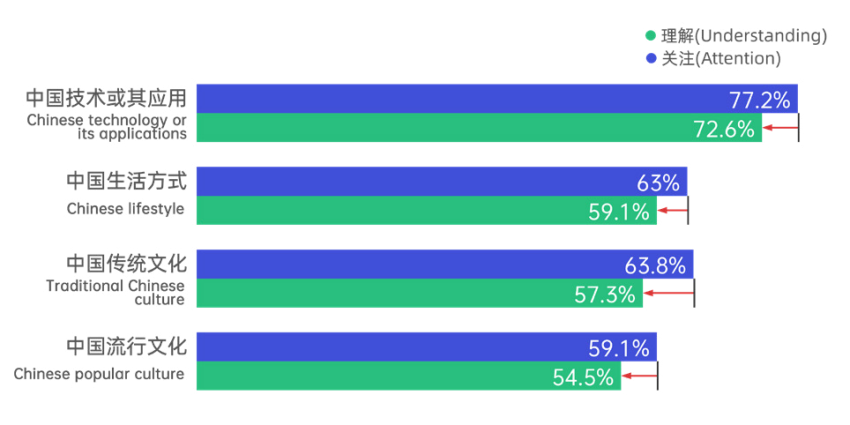
Figure 3.2 Comparison of Attention and Understanding Levels across Chinese Cultural Sub-domains
Global respondents present a diversified cognitive landscape regarding the characteristics of Chinese civilization and culture. Being innovative receives the highest recognition, with 60.6% viewing it as an important feature of Chinese culture, which highly corresponds with contemporary China's technological development and social transformation. Continuity ranks second, gaining recognition from 45.8% of respondents, reflecting the widespread global acknowledgment of the historical heritage of Chinese civilization. Unity receives 33.7% recognition, peacefulness gains 33.7% recognition, while inclusiveness receives relatively lower recognition at 26.1%. This distribution demonstrates the international community's high recognition of Chinese culture's innovative capacity and historical heritage characteristics, while also revealing that understanding of Chinese culture's inclusive nature requires further strengthening.
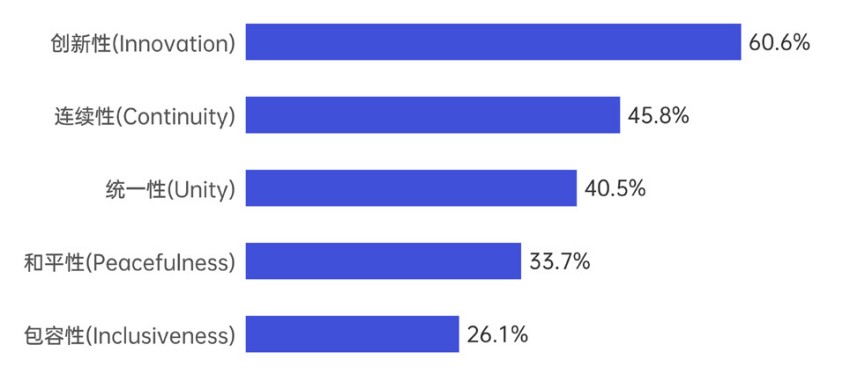
Figure 3.3 Perception of Chinese Cultural Characteristics
The diverse choices of channels for obtaining information about Chinese culture demonstrate that digital media platforms hold a dominant position. Social media has become the primary avenue for respondents to learn about Chinese culture, accounting for 53.4%, fully reflecting the profound transformation in cultural dissemination patterns in the new media era. Film and television media follow closely behind at 46%, demonstrating the significant role of audiovisual cultural products in cross-cultural communication. The proportion using Chinese products and services as channels for cultural understanding reaches 35.9%, reflecting the practical influence of consumer experience on cultural transmission. Chinese companies in their home countries serve as information channels at 18.5%, embodying the cultural dissemination function carried by Chinese enterprises in their overseas operations.
The influence of traditional channels remains relatively limited. Among these, cultural activities in their home countries account for 16.6%, reading books 16.7%, Chinese friends or colleagues 15.6%, travel experiences to China 14.7%, museum or cultural heritage visits 12.5%, recommendations from friends and family 11.3%, and school education 10.6%. This distribution pattern of channels highlights the central position of digital media and audiovisual cultural products in the international dissemination of Chinese culture, while also reflecting the challenges and transformation needs that traditional cultural exchange methods face in the new media environment.
II.International Perception of Chinese Cultural Exchange and Contributions
Global respondents highly affirm the global influence of Chinese civilization and culture. Survey results indicate that 81.6% of respondents believe China's global cultural influence and soft power are growing, while 78.6% consider Chinese culture attractive. This demonstrates that Chinese culture enjoys broad recognition and positive influence overseas, laying a solid foundation for the further global dissemination of Chinese culture.
Global respondents also generally hold positive views regarding China's cross-cultural exchange practices. Nearly three-quarters of respondents (74.1%) believe that China's civilizational and cultural exchanges with other countries follow the principle of mutual benefit, 69.6% of respondents consider that China has promoted global cultural exchange, and 65.8% of respondents acknowledge the contribution of Chinese values to building multicultural consensus.
Global respondents highly recognize China's openness in cultural exchange. 64.3% of respondents believe that Chinese culture is open to the outside world and eager to learn from other cultures, 64.8% of respondents consider that China's visa policies have promoted international cooperation and exchange, and 64.5% of respondents believe that China never imposes its own culture or values on others.
Global respondents hold Chinese civilization itself in high regard for its overall contribution to the development of world civilization and culture. 75.4% of respondents believe that Chinese civilization has contributed to the development of world civilization, 70.1% of respondents consider that China has promoted mutual learning and exchange among civilizations, 70.6% of respondents believe that Chinese civilization has provided new perspectives for global governance, and 70.3% of respondents consider that Chinese values offer certain reference value for countries of the Global South.

Figure 3.4 Assessment of Chinese Civilization's Contributions
Consistent with the aforementioned data on attention to and recognition of Chinese cultural elements, global respondents' perceptions of specific areas of Chinese civilization's contributions show a similar differentiated distribution. 51.3% of respondents regard science, technology, and inventions as important contributions of Chinese civilization to the world, reflecting China's international influence in technological innovation. Economic development models rank second at 33.8%, culinary culture receives recognition from 31% of respondents, and medical and health concepts gain acknowledgment from 25.6% of respondents.
However, recognition of contributions in abstract concepts remains relatively low. Philosophy and values account for 16.2%, the tradition of valuing education for 16.1%, the concept of harmonious coexistence receives 14.3% recognition, and literature and arts account for 14%.
Based on the aforementioned findings, global respondents demonstrate significant recognition of the international influence of Chinese civilization and Chinese culture, fully reflecting the extensive influence and appeal of Chinese civilization in the international community. Respondents generally acknowledge China's adherence to the principle of mutual benefit in cross-cultural exchanges, highly commend China's role in promoting global cultural exchange and the contribution of Chinese values to building multicultural consensus, while positively evaluating the openness of Chinese cultural exchange, believing that Chinese culture is open to the outside world and eager to learn from other cultures, never imposing its own culture or values on others.
However, respondents' perceptions of specific areas of Chinese civilization's contributions exhibit distinctly differentiated characteristics. Material cultural contributions such as science and technology have gained more intuitive recognition and widespread acknowledgment, while international awareness of abstract cultural concepts such as philosophical values and the concept of harmonious coexistence remains relatively low. This phenomenon suggests that China needs to place greater emphasis on the dissemination and understanding of spiritual and cultural connotations in the process of deepening exchanges and mutual learning with civilizations around the world, so as to better facilitate profound dialogue between China and different civilizations.
III.Prejudices Against Chinese Culture
In contrast to the widespread recognition of Chinese cultural influence, respondents showed divergent perceptions regarding cultural similarities. Survey results indicate that 43.8% of respondents believe there are significant differences between Chinese culture and their own national culture, 28.7% consider the two cultures to have both similarities and differences, while only 24.2% regard the two cultures as similar. This differentiated perception reveals the complexity of international dissemination of Chinese culture, namely the need to seek consensus in exchanges while acknowledging cultural differences.
The objective existence of cultural differences often tends to evolve into subjective prejudices. Data shows that 72.1% of respondents agree that many people hold prejudices against Chinese culture. These findings reveal stereotypical cognitive patterns toward Chinese culture within Western discourse systems, particularly misinterpretations regarding issues such as political systems and individual rights.
Regarding the causes of prejudice, respondents demonstrate relatively clear understanding. Data shows that 52% of respondents consider ideological bias as the primary cause of prejudice against Chinese culture, 51.8% of respondents cite cultural differences, 46.2% regard misleading media coverage as a significant factor, and 36.3% point to the influence of differences in historical narratives. These results reflect the profound impact of politicization tendencies and media bias on cultural perception within the current international public opinion environment.
In this regard, respondents consider diversified exchange approaches as the most important means of eliminating prejudice. 48.3% of respondents believe academic exchanges and cooperation constitute an effective way to eliminate prejudice, 46.4% support promoting interpersonal exchanges, and 45.7% advocate for China to conduct more cultural activities. Meanwhile, 39.3% of respondents consider business and international organizational initiatives to play important roles, 38.6% value the function of school education, and 35.8% support greater use of social media. These findings demonstrate that equal dialogue, openness and inclusiveness, and mutual learning constitute practical pathways widely endorsed by global populations for bridging cultural divides and eliminating prejudice. They also confirm that strengthening public understanding of Chinese civilization across nations requires breakthroughs through multi-level and multi-dimensional people-to-people exchanges.